🍭 Coretime Sale Price Simulator
Welcome to the Coretime Sale Price Simulator 🎉 🎉 🎉! This interactive tool allows you to simulate and visualize the sale price of Lastic cores over time based on various parameters.
Accessing the Application
Visit lastic.streamlit.app to start using the application. Or go to check the Github repository.
Features
The Lastic Sale Price Simulator offers the following features:
- Interactive sliders to adjust sale parameters.
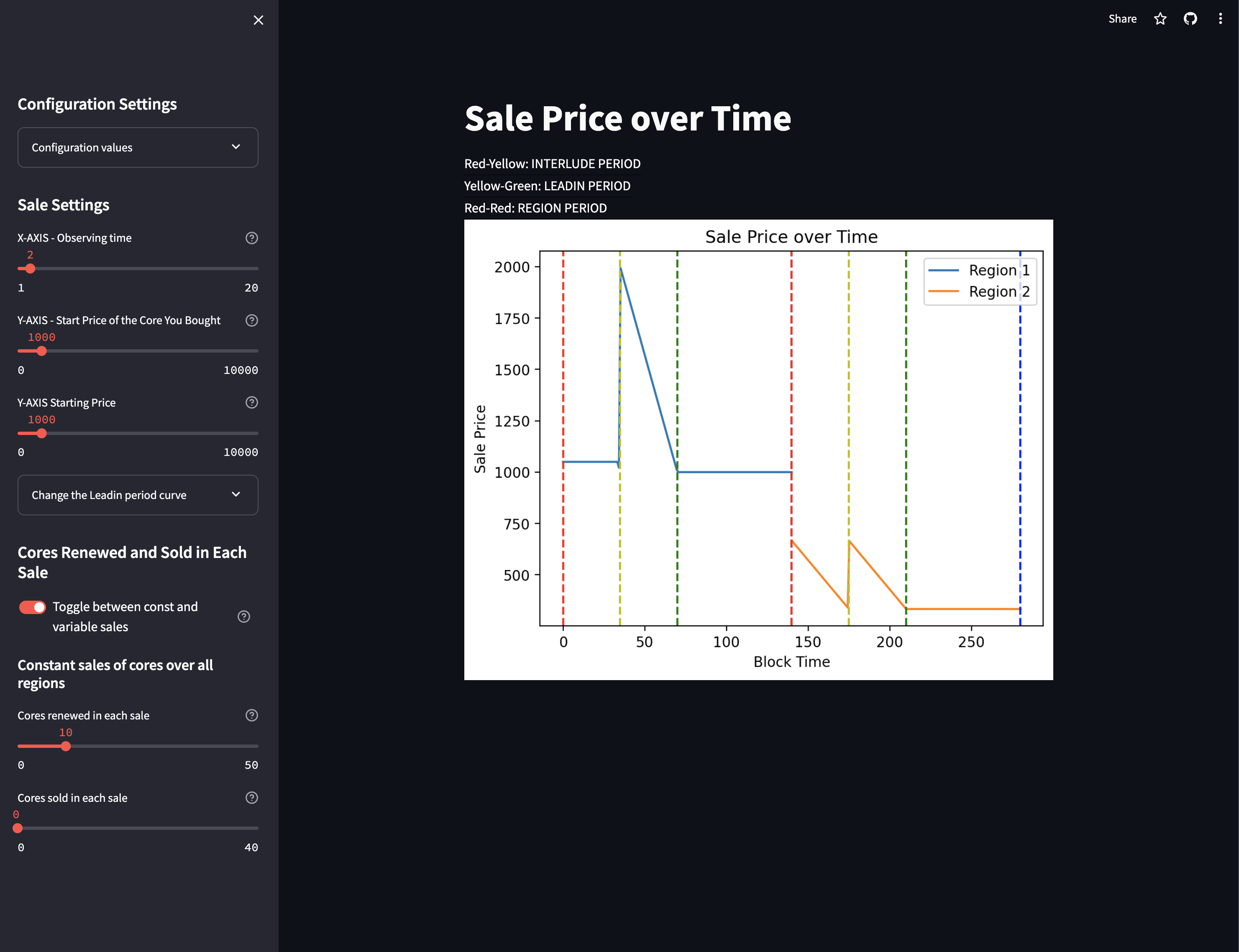
- Real-time graph visualization of sale prices over time.
- Options for configuring core sales, including constant and variable sales settings.
- Ability to observe sale price changes over different regions and time periods.
A few explainations before diving deeper
Before you start diving deeper into how to use the tool, here is an article breaking down RFC-1, that gives explainations to what the proposed changes regarding Polkadot and it's core allocation.
In addition to that here are a few key things to know:
Overview of Agile Coretime on Polkadot
Agile Coretime introduces a new, flexible method for allocating "Coretime" or "block space" within the Polkadot Network. This system shifts from a fixed, long-term allocation model to a dynamic, sale-based approach, providing more versatility and efficiency in resource utilization.
Key Concepts
Polkadot Ubiquitous Computer (Polkadot UC): Represents the collective computing resource provided by the Polkadot Network. It's a resilient, multi-core virtual machine that runs WebAssembly.
Coretime: Analogous to block space, Coretime is the time during which a Polkadot core is dedicated to performing a specific task. It's a measure of computational resource allocation within the network.
Coretime chain: This is a system parachain proposed that will keep track of Coretime transactions. It will allow users to buy Instantanious Coretime credits, buy Bulk Coretime, allocate it to certain tasks etc. The main goal of the Coretime chain is to transfer the computational load from the primary Relay chain to the Coretime system parachain.
Instead of fixed, long-term allocations (like the previous parachain slot auctions), Coretime is periodically sold in two formats:
Bulk Coretime: Scheduled and sold in advance for a set period. It allows for planning and stable allocation of resources.
Instantaneous Coretime: Sold on a block-by-block basis, catering to immediate, short-term needs.
This dual system aims to balance long-term planning with the flexibility of immediate resource allocation. Since this price simulator only models Bulk Coretime pricing, we are going to focus only on explaining Bulk Coretime and not Instantanious Coretime.
Region: The Tradable Unit of Coretime
- A Region is a defined period of Coretime with a specific regularity and core association, forming the basis of the sale and allocation process.
- Regions can be traded, split, or pooled, providing flexibility in how Coretime is managed and utilized.
Simplified Explanation of Bulk Pricing in Polkadot's Agile Coretime
The pricing of Bulk Coretime in Polkadot's network follows a dynamic model that adapts based on several factors. This section simplifies the understanding of this pricing mechanism.
Key Components of Bulk Price Setting
OLD_PRICE: Price of Coretime in the previous sale.BULK_TARGET: Ideal number of cores aimed to be sold or renewed.BULK_LIMIT: Maximum number of cores available for sale or renewal.CORES_SOLD: Actual number of cores sold or renewed in the last sale.SELLOUT_PRICE: Price at which the last Bulk Coretime was sold, affecting the next sale price.
How Prices Change
- Increase and Decrease: The price of Coretime increases as sales approach
BULK_LIMITand decreases as they move closer to zero. - Stability at Target: If the number of cores sold equals the
BULK_TARGET, the price is expected to stay stable. - Edge Case Handling: In situations where no new sales occur but renewals exceed the target, the price remains unchanged.
Example Formula
An example formula to demonstrate this dynamic pricing is:
Calculate EFFECTIVE_PRICE based on `SELLOUT_PRICE` and `CORES_SOLD`.
NEW_PRICE is determined by comparing `CORES_SOLD` with `BULK_TARGET` and `BULK_LIMIT`.Calculate EFFECTIVE_PRICE based on `SELLOUT_PRICE` and `CORES_SOLD`.
NEW_PRICE is determined by comparing `CORES_SOLD` with `BULK_TARGET` and `BULK_LIMIT`.Pricing During the Leadin Period
During the initial phase of a sale, known as the Leadin Period, the price of Coretime starts higher and gradually reduces to the Sale Price by the end of the period.
- Price Reduction: The price decreases linearly from twice the Sale Price at the start of the Leadin Period to the Sale Price at its end.
- Formula:
PRICE := SALE_PRICE * (2 - ((Current Time - LEADIN_BEGIN) / LEADIN_PERIOD))
Parameters Influencing Pricing
Some parameters influencing this pricing model include:
| Parameter | Value | Type |
|---|---|---|
BULK_PERIOD | 28 * DAYS | Specified |
INTERLUDE_PERIOD | 7 * DAYS | Specified |
LEADIN_PERIOD | 7 * DAYS | Specified |
TIMESLICE | 8 * MINUTES | Specified |
BULK_TARGET | 30 | Suggested |
BULK_LIMIT | 45 | Suggested |
RENEWAL_PRICE_CAP | Perbill::from_percent(2) | Suggested |
This simplified explanation aims to provide a clearer understanding of how Bulk Coretime pricing operates within the Polkadot network, making it easier to engage with the Coretime Sale Price Simulator.